Our Services
What is Orthopedics? MGM Medical Centre
Orthopedics is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions related to the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments. At MGM Medical Centre, our expert orthopedic specialists provide comprehensive care to help you manage musculoskeletal issues, from fractures to joint replacements. Whether you’re dealing with an injury or chronic pain, our team is dedicated to offering the best orthopedic treatments for your health and well-being.
Types of Orthopedics
Orthopedics is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Below, we explore the various types of orthopedic specialties to help you better understand the services offered by orthopedic professionals.
Symptoms That May Need Orthopedic Care
Orthopedics focuses on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, and tendons. Recognizing the symptoms early can help you seek proper orthopedic care and prevent long-term issues. Below are common symptoms that may require a visit to an orthopedic specialist:
1. Persistent Joint Pain
2. Limited Range of Motion
3. Numbness or Tingling
4. Chronic Back or Neck Pain
5. Stiffness in Joints
6. Swelling or Inflammation
7. Muscle Weakness
8. Bone Deformities
9. Difficulty Walking or Standing
10. Fractures and Trauma Injuries
Common Reasons for Orthopedic Problems
Orthopedic problems can arise from a variety of factors, affecting the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments that make up the musculoskeletal system. Understanding the reasons behind these issues can help in seeking proper orthopedic care and taking preventive measures. Below are some of the most common causes of orthopedic problems.
1. Aging and Degeneration
2. Genetics and Family History
3. Poor Posture
4. Infections and Diseases
5. Occupational Factors
6. Injury or Trauma
7. Overuse and Repetitive Movements
8. Obesity
9. Lack of Physical Activity
10. Inflammatory Conditions
Treatments for Orthopedic Problems
Many orthopedic issues can be managed without surgery. Non-surgical treatments are often the first step in the care process. These may include:
- Physical Therapy: One of the most effective treatments for orthopedic problems, physical therapy helps strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can be prescribed to manage symptoms of orthopedic issues, providing temporary relief.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For conditions like arthritis, orthopedic specialists may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and provide long-term relief.
- Bracing and Splinting: To protect joints and bones, braces and splints can help immobilize the affected area, promoting healing and preventing further damage.
When conservative treatments don’t provide sufficient relief, surgery may be recommended. Common orthopedic surgeries include:
- Joint Replacement Surgery: For patients with severe arthritis or joint degeneration, joint replacement surgeries like hip and knee replacements can offer significant pain relief and restore mobility.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive technique used to treat joint problems, such as torn cartilage or ligament injuries, arthroscopy involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the procedure.
- Spinal Surgery: In cases of severe back pain or herniated discs, spine surgery may be needed to alleviate pressure on nerves and restore spinal function.
- Fracture Repair Surgery: Broken bones may require surgical intervention, such as the placement of pins, plates, or screws, to ensure proper healing and alignment.
Orthopedic specialists are increasingly using regenerative medicine techniques, including stem cell therapy, to promote healing in joints, tendons, and ligaments. These treatments can help reduce inflammation, regenerate tissue, and slow down degenerative changes.
PRP therapy involves using a patient’s blood to concentrate platelets, which are then injected into the affected area. This treatment promotes healing by enhancing tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
After surgery or injury, orthopedic rehabilitation programs are crucial for recovery. Rehabilitation specialists guide patients through exercises and techniques to restore strength, mobility, and function, helping them return to their normal activities as quickly as possible.
6. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is used in some orthopedic treatments to reduce pain and inflammation. It can help with conditions like tendinitis, sprains, and joint stiffness by promoting tissue repair and improving circulation.
7. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT)
Orthopedic specialists trained in osteopathy may use OMT techniques to treat musculoskeletal issues. This hands-on approach involves using the hands to diagnose, treat, and prevent orthopedic conditions, such as back pain, joint problems, and muscle tension.
8. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors specializing in orthopedics can help with spinal alignment, joint mobility, and musculoskeletal issues. Chiropractic adjustments can relieve pain and improve function, especially for patients with back and neck problems.
9. Custom Orthotics
For patients with foot and ankle problems, custom orthotics can be prescribed to provide support, realign joints, and reduce pain. These specially designed shoe inserts can address issues like flat feet, plantar fasciitis, and other foot deformities.
Diagnostic Tests for Orthopedic Problems
Orthopedic diagnostic tests are essential for identifying the root causes of musculoskeletal issues, and helping orthopedic specialists create effective treatment plans. These tests assess the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments to ensure proper diagnosis and care. Below are some of the most common diagnostic tests used in orthopedics to detect and evaluate orthopedic problems.
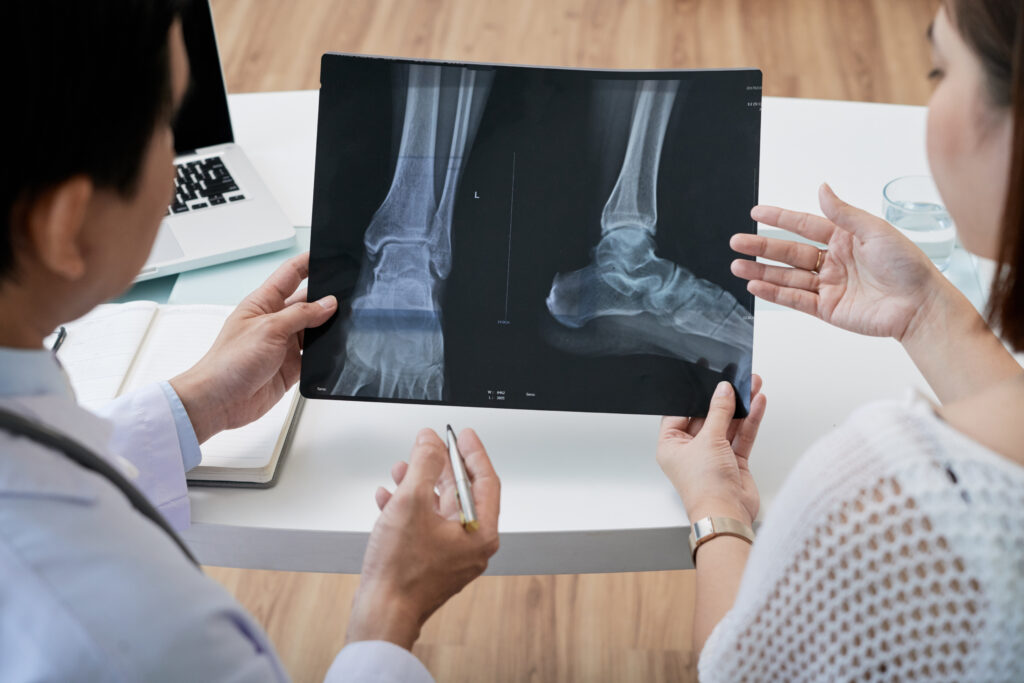
1. X-rays
X-rays are one of the most widely used orthopedic diagnostic tools. They provide clear images of bones, joints, and fractures, making them invaluable for detecting fractures, arthritis, and joint deformities. Orthopedic specialists often use X-rays to identify structural problems in the musculoskeletal system.
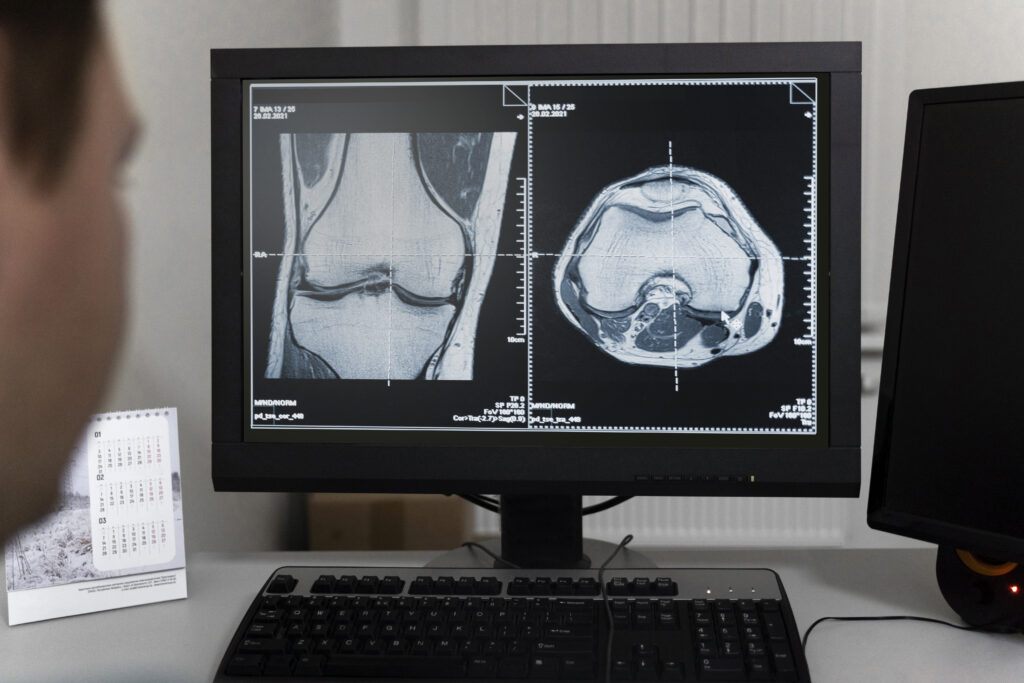
2. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is a non-invasive test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This test is crucial in diagnosing soft tissue injuries, cartilage damage, and spinal issues. MRI is frequently used in orthopedics for diagnosing conditions that may not show up on X-rays.
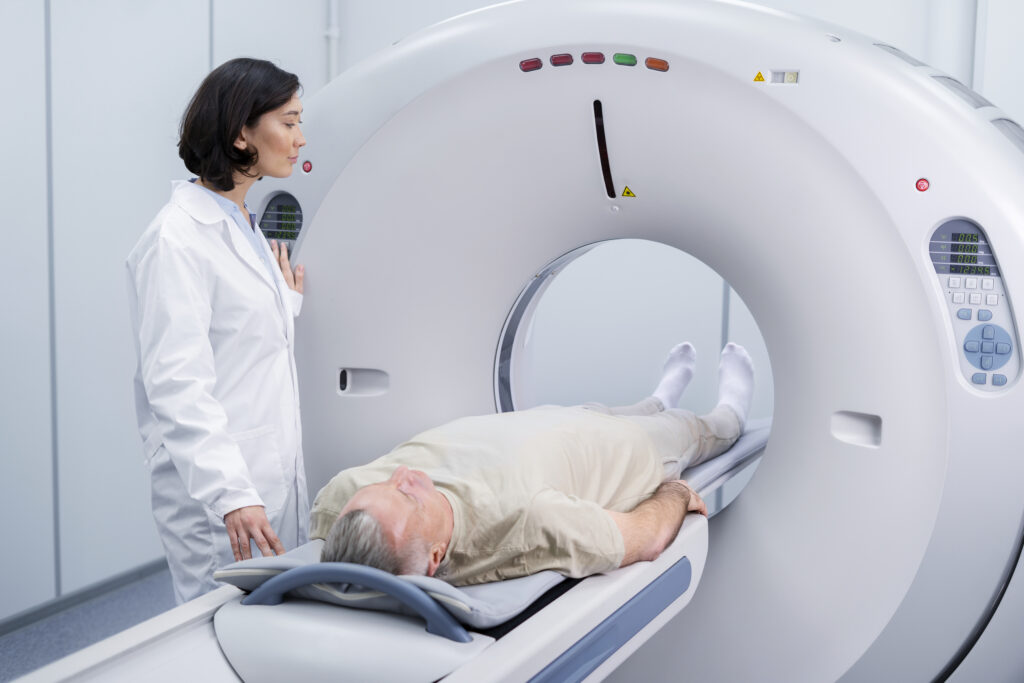
3. CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
A CT scan combines X-rays and computer technology to create cross-sectional images of the body. It’s especially helpful for diagnosing complex fractures, bone tumors, or joint problems that might not be visible with regular X-rays. Orthopedic specialists use CT scans to get a more detailed look at bones and joints.
4. Bone Scans
Bone scans are used to detect bone infections, inflammation, or cancer. This test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the bloodstream, which helps highlight abnormal areas in the bones. Orthopedic experts often rely on bone scans when other tests, like X-rays, don’t provide enough information.
5. Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues and muscles. It’s commonly used in orthopedics to examine tendons, ligaments, and muscles, especially for injuries or inflammation. Ultrasound is often used to guide injections or to assess joint and soft tissue health.
6. Electromyography (EMG)
EMG is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. It helps orthopedic specialists assess nerve function and diagnose conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, herniated discs, or muscle disorders. It provides important information for orthopedic treatment plans.
7. Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where an orthopedic surgeon inserts a small camera into the joint to examine its internal structures. It’s often used to diagnose and treat joint problems, such as cartilage tears, ligament injuries, and arthritis. This diagnostic test allows orthopedic specialists to visually inspect the joint and make real-time treatment decisions.
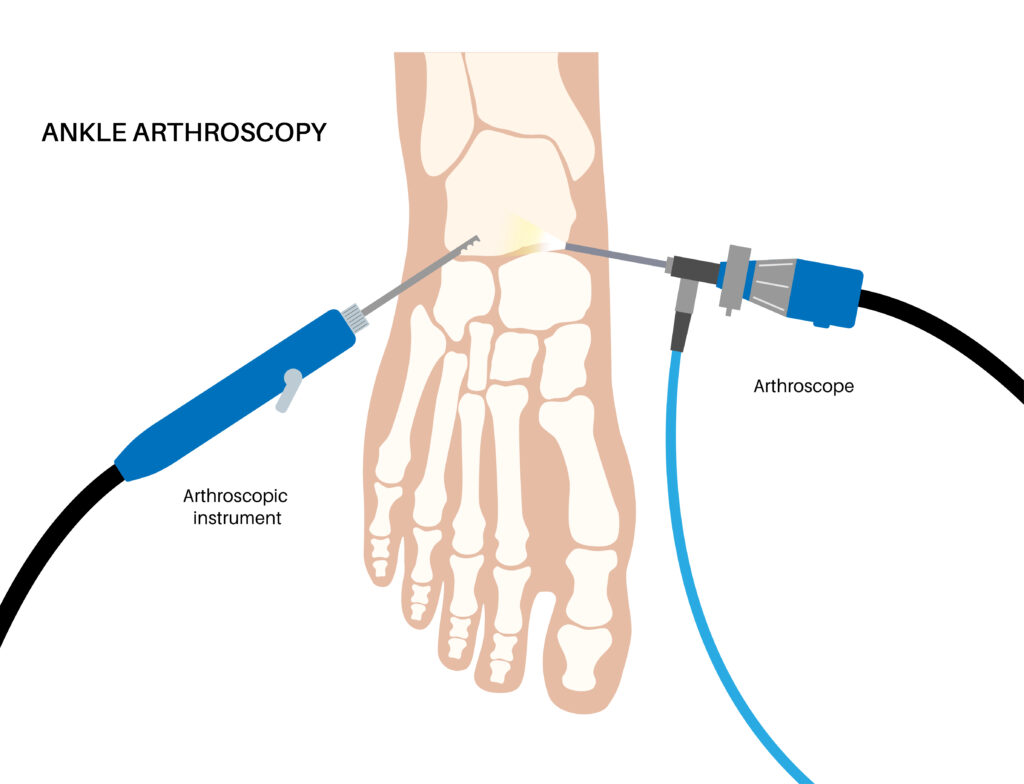
8. Bone Density Test
Bone density tests, such as DXA scans, are used to measure the strength and density of bones. These tests are important in diagnosing osteoporosis and determining the risk of fractures. Orthopedic professionals rely on bone density tests to monitor bone health and prevent fractures.
9. Joint Fluid Analysis
In this test, a sample of fluid is drawn from a joint to check for signs of infection, inflammation, or arthritis. This diagnostic procedure is especially useful in diagnosing conditions such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis. Orthopedic specialists use joint fluid analysis to confirm a diagnosis and guide treatment.
10. Blood Tests
Blood tests may be used in orthopedics to check for underlying conditions that affect the bones and joints, such as infection or inflammatory disorders. While blood tests alone cannot diagnose musculoskeletal problems, they can provide valuable information that complements other orthopedic diagnostic tests.

FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Orthopedic medicine focuses on the care and treatment of problems related to the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments. It involves diagnosing and treating injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system to help improve mobility and relieve pain.
Orthopedic surgeons treat a variety of conditions, including sports injuries, arthritis, joint problems, fractures, spine conditions, and other musculoskeletal issues. They also manage chronic pain from conditions like osteoarthritis and perform surgeries like joint replacements when necessary.
Orthopedic surgery may be necessary when non-surgical treatments, like physical therapy or medication, don't provide relief. Conditions such as severe fractures, torn ligaments, joint degeneration, or spinal issues may require surgery for long-term improvement.
After orthopedic surgery, patients can expect some swelling and discomfort, which is normal. Your doctor will provide instructions on how to manage pain, prevent complications, and begin physical therapy. Recovery time varies depending on the surgery but typically includes rest and gradual rehabilitation.
Recovery times vary based on the type of surgery and your overall health. Some patients recover within weeks, while others may take several months. Following your orthopedic surgeon’s care plan and attending physical therapy are key to ensuring a smoother recovery process.


